Price-Earnings Ratio (P/E Ratio)
People that own a business are called shareholders because they own part (or share) of a business. Anybody that buys shares in a business is known as a shareholder. Shareholders are interested in how much money (return) the firm will make for them. Shareholder ratios calculate the return shareholders receive from the money they have invested in a firm; in this article we will discuss the shareholder ratio called The Earnings Ratio (price/earnings ratio, sometimes referred to as P/E ratio or PER).
Click to learn about the Earnings Per Share Ratio and The Dividend Yield, the other shareholder ratios.
What Is The Price - Earnings Ratio
The Price - Earnings Ratio (also known as the PE ratio) analyses the firm's current share price against how much money each share is generating. This gives investors an idea about the likely returns (money) they could make if they decided to buy shares in the firm.
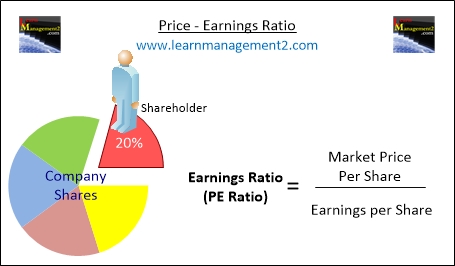
How To Calculate The Price - Earnings Ratio
To calculate The Price - Earnings Ratio find out
- The market price per share and
- The earnings per share
Divide the market price per share by the earnings made by share.
Price - Earnings Ratio Market Price per Share (pence/cents)
= _________________
Earnings per Share (pence/cents)