Sole Trader (Sole Proprietorship)
Related Links
Business Types | Companies and Firms | Partnerships | Co-Operatives | Franchises | Charities |
Sole Trader Introduction
A large number of people setting up a new business will create a sole trader business. A sole trader business (which is sometimes called sole proprietorship) is a business owned by one person, although the organisation may employ more than one person. A sole trader is self employed and is therefore responsible for how well the business does.
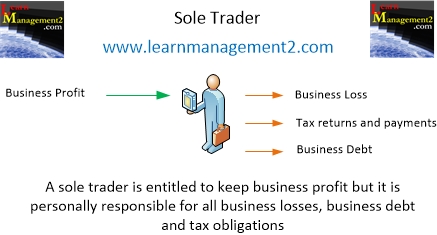
Business Profits, Losses and Liabilities
A sole trader is entitled to keep all of the profits the business makes after paying all of the taxes that are due on it. However this also means that are a sole trader is responsible for all losses made by the business; their liability is not limited as would be the case for example for a Limited Company or a Limited Liability Partnership.
The image below shows the things sole traders are liable for and the things they benefit from.
Sole Trader Business Name
The sole trader is free to choose whatever name they would like for their business as long as
- The sole trader business name is not offensive
- The sole trader business name is not an existing business name protected through intellectual property such as a trademark or copyright
- The sole trader business name implies that the business is not a sole trader for example by using the words limited, Ltd, public limited company, PLC.
To safeguard against legal proceedings the sole trader should ensure that they don't use a name registered to someone else.
Setting Up A Sole Trader Business
A sole trader business is the simplest type of business to establish. Usually there are no legal restrictions affecting the establishment of a sole trader business.
There may be schemes that the sole trader may need/want to register with for example
- The construction industry scheme operated by the HMRC in the UK
- A trading standards scheme to endorse the business as "competent" and "trustworthy".
- A criminal record check if the sole trader and its employees will be working with children and vulnerable people
- Applicable data protection schemes if the business will be retaining personal data
It is also prudent for sole traders to have the correct business insurance such as public liability, professional indemnity, and buildings insurance.
Sole Traders Business Records And Accounts
A sole trader does not need to keep accounts, but it should ensure that it has registered the business with the relevant tax authority. For example in the UK a sole trader has to register the business with the HMRC's self assessment tax return. Although sole traders do not need to keep accounts they will have to keep
- records of business income and expenses so that they can submit any tax returns that are due
- records showing personal income, savings and investments
- records of employee pay, taxable benefits, holidays and sickness
To minimise tax liability sole traders may employ accountants to complete tax returns on their behalf and for advice on how to minimise tax lawfully ( tax avoidance not tax evasion).